Combat Arts Tricep Injuries Overview
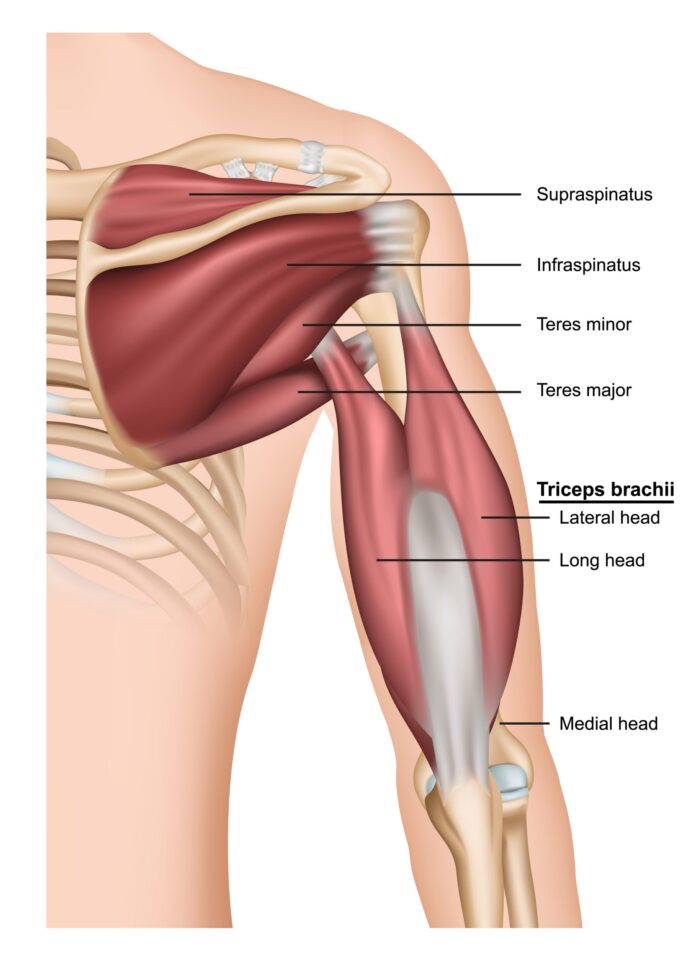
If you see any pictures of Sergio Moraes, the MMA fighter, then you will notice, he’s missing a part of his triceps or that’s what it looks like. This is what happens when the triceps muscle experiences a tear and never recovers or has no treatment. The triceps are the large, thick muscle in the bottom part of the forearm. Its main function is to extend the forearm at the elbow joint.
Tricep Injury Causes
Overtraining and olecranon bursitis play some role in a triceps tear. Increased shoulder flexion causes the long head of the triceps to stretch considerably. This increases the load on the tendon. In a martial artist, this is common among those who fall on an outstretched hand. The sudden deceleration puts additional stress on a contracted triceps muscle while the elbow is in extension. It also occurs while doing dips or bench presses. Also hitting or jabbing with a posterior elbow can cause the triceps to tear as it meets with fixed resistance.
Tricep Injury Symptoms
Types of Tricep Injuries
The main injury involving the triceps is a tear. Typically, it’s considered too common among users of anabolic steroids but is also precipitated by overuse. Triceps tendinopathies do occur among MMA fighters but are not as common as tendinopathies of the knee or shoulder.
Focusing on Arm Strength Can Help Prevent & Manage Tricep Injuries
Subscribe for More Helpful Advice!
Related Injuries
Triceps Tears
The triceps typically have three heads which is how it gets its name. It is located in the dorsal section of the arm. Triceps tears are rarer compared to triceps tendonitis. Having chronic metabolic conditions like diabetes and parathyroid disease increases the chances of triceps tear.
Tricep Tears Symptoms
Tricep Tears Causes
A triceps tendon tear or avulsion can take place during a fight on receiving a direct blow to the elbow or falling on an outstretched arm against resistance. Ruptures or avulsions occur at the tendon-bone junction. This due to the eccentric contraction of the muscle. A fighter will experience a painful popping sensation. This is followed by pain and swelling over the posterior elbow. Many fighters will find they cannot extend the elbow against resistance.
To learn how Triceps tears is diagnosed Click Here
Common Tricep Injuries
Other common triceps injuries like tendonitis is fairly common and explained in detail in our Common Injuries section.
Tricep Injury Diagnosis
The diagnosis of triceps injuries tends to be clinical. Plain films will only reveal if there is an underlying fracture. An ultrasound or MRI would be more diagnostic to identify tears in the triceps muscle.
Injury Specific Diagnosis
Triceps Tears
Physical Exam
The physical exam involved isolating the muscle and testing it. The triceps reflex is also tested by sharply striking the triceps tendon. The fighters’ shoulder and elbow are abducted to 90 degrees. Then with a reflex hammer, the triceps tendon is tapped. Usually, the reflex remains intact since the cervical nerves are responsible for the reflex.
Imaging
Plain films and MRI capture complete and partial tears of the triceps muscle and tendons. On an X-ray acute tendon tears are seen as bony flecks. This suggests a triceps avulsion injury. It can also be seen on an ultrasound.
For fighters who do not have a complete avulsion, the rupture takes place at the bone tendon junction. They cannot be visualized on plain films. Both ultrasound and MRI are used to diagnose complete tears and partial tears where the olecranon attachment is not involved. Ultrasound is as accurate as MRI for both complete and partial ruptures. They are also useful to identify the location of rupture.
Ultrasound is done with the elbow flexed. It shows reduced echogenicity and calcification. MRI can detect abnormalities in tendinopathies. For a snapped triceps, US, MRI, CT, and sonoelastography are all used. Ultrasound is the imaging modality of choice for some as it allows differentiation between tendons and nerves.
Lab Tests
Lab tests are uncommon. The blood tests usually involve looking for metabolic disorders. They include CBC, Hba1c, Urine micro albumin, calcium, phosphorus, PTH, and Vitamin D.
To learn how Triceps tears is diagnosed Click Here
Diagnoses of Common Tricep Injuries
Learn more about how physicians assess injuries through visual inspection, lab tests, x-rays, and other methods in our Common Diagnoses section.
Tricep Injury Treatment
The management of triceps injuries depends on the type of injury. Tendinopathies require strengthening of the triceps and decreasing pain. Physical therapy which includes isometric exercises and clap push-ups are helpful. For tears, the management is surgical, and depends on the type of tear.

Injury Specific Treatment
Triceps Tears
Emergency
Triceps tears are not medical emergencies. Sometimes, it takes a while for an athlete to identify an injury. If there is no visible deformity, a fighter might disregard the injury as elbow pain. The important step is to identify the injury. Therefore, any pain or symptoms must be referred to an orthopedic doctor right away.
Medical
The treatment for tears is usually surgery. If there is considerable weakness of elbow extension, then surgical repair is advised. For small partial tears, non-operative management has a good prognosis.
Wear a brace with slight 30⁰ flexion for about 7 weeks. Avoid pushing, resistance, or heavy lifting for about 12 weeks. Alternative treatments like platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injection has been successfully used for the treatment of partial tears.
In acute tears of more than 50%, surgical repair is better. Treating chronic ruptures is challenging. Reconstruction with a graft from the Achilles, plantaris, semitendinous, aconeus, latisimus dorsi can be done. Where the triceps are completely avulsed, surgery is advocated. This involves the repair of the avulsed triceps tendon with a Krakow suture pattern to the olecranon. It is done via bone tunnels.
Home
Avoid the provoking activity for 3-6 months. Reduce pain by doing single-arm triceps press down. This is held in a mid-position of 45⁰ elbow flexion. Do it for 45 seconds without shaking. Allow 2 minutes for recovery.
Simple exercises that help include simple rope triceps press-downs. Four sets of 6 repetitions are enough. High volume exercises with heavy eccentric loads are also helpful. These include single-arm triceps press-downs that use two hands to push the weight down and one on the eccentric.
Common Tricep Treatments
Learn more about how healthcare professionals treat injuries using physical therapy, medications, surgery, and other approaches in our Common Treatments section.
