Combat Arts Lower Back Injuries Overview
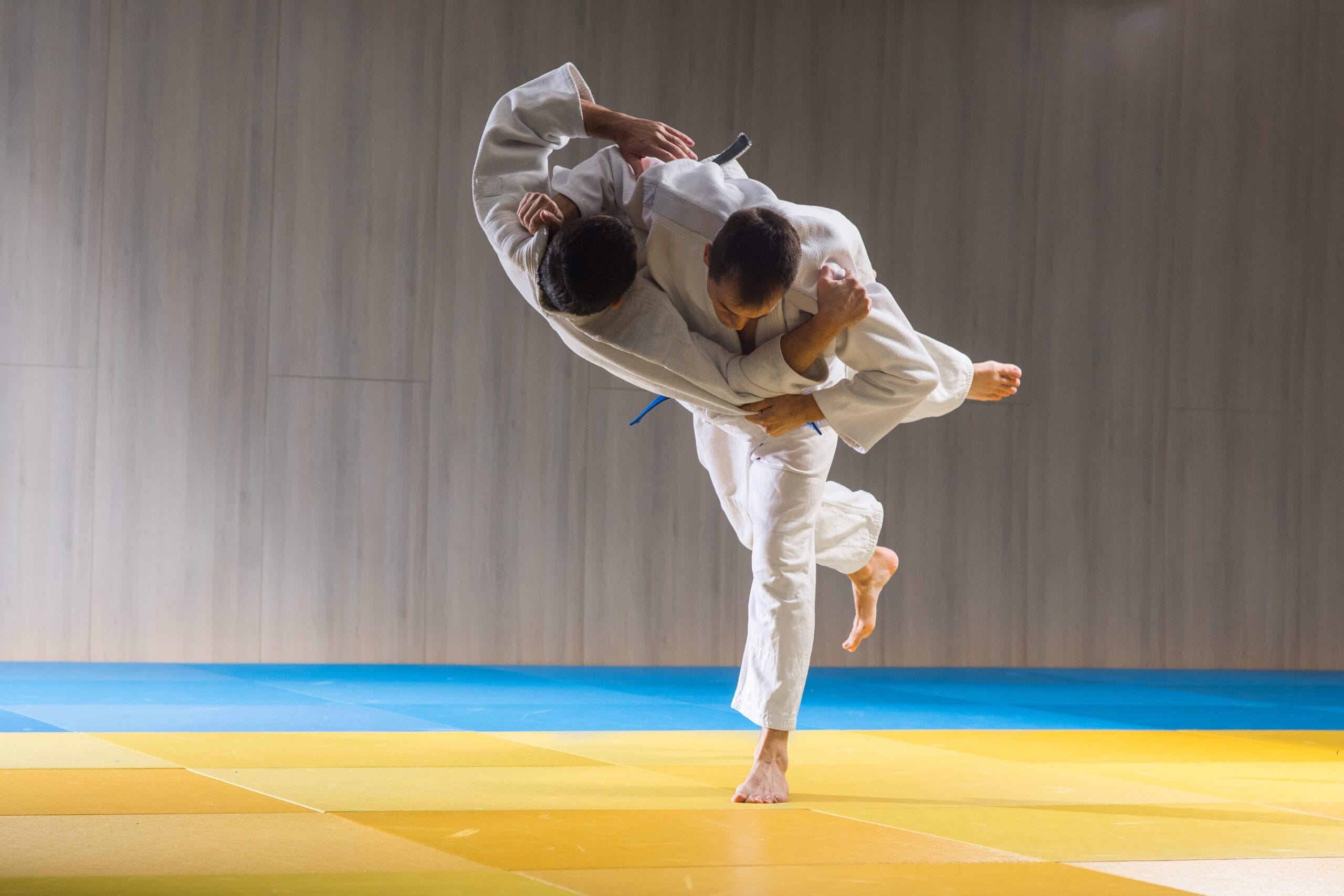

Jet Li cracked his fifth vertebrae, suffered a broken rib, fractured his left ankle, and had internal injuries after falling 12 feet from a set tower in filming Fearless in 1986, plus he’s had many smaller injuries in his life as a martial artist.
Now he’s dealing with heart issues and hyperthyroidism, as well. Li said, ‘I’m in pain but I’m not in a wheelchair yet.’
Lower Back Injury Causes
There are several physical issues that can cause problems: Weak lower back muscles, weak abdominal muscles, overly tight or weak psoas muscle, overly tight or weak hip flexor muscles, and/or overly tight or weak hamstring muscles.
Overworking these muscles through fights, five-round training camps, and heavy training can also injure the spine via vertebral fractures. Additionally, kicks, punches, and chokes that cause the back to hyperextend can damage the ligaments. Submission moves like the swim move in jiu-jitsu where the back is mounted and stretched can strain the back.
Lower Back Injury Symptoms
Types of Lower Back Injuries
Injuries to the spine are common due to the constant wear and tear on the spine and its muscles and ligaments. These injuries can worsen to the point the spine can herniate and be life-threatening. Other back injuries like herniated discs and fractured vertebrae have been covered in the neck area. In this section, we focus on back injuries specific to the lower back like sciatica and cauda equina syndrome.
Weak Lower Back Muscles or Abdominal Muscles? Overly Tight or Weak Psoas Muscle? Weak Hip Flexor Muscles? Overly Tight or Weak Hamstring Muscles?
What's Causing Your Back Pain? We Can Help!
Related Injuries
Sciatica plagues many fighters. MMA great Cain Velasquez has been battling sciatica for over four years. In his case, the sciatic nerve was being compressed by bony spurs. Even standing up for fifteen minutes for painful. He could barely manage to do everyday physical tasks. He had surgery and it didn’t work. Then he had another surgery to make room for the nerve. This time it was successful and led to his return to the Octagon.
Symptoms
Causes
The sciatic nerve is made up of nerve roots from the L4 to S2 vertebra. The nerve roots fuse to form the large sciatic nerve. The sciatic nerve runs a long course after it exits the pelvis through the sciatic foramen posteriorly to the posterior thigh and ends at the knee posteriorly in the popliteal fossa. There it breaks into tibial and fibular nerves. Any problems affecting the nerve along this path can cause sciatica. Injuries to the spine like herniated disc, bone spurs on the spine, or spinal stenosis which narrows the spinal column can compress the nerve. The injuries could be due to overuse or blunt trauma from high-velocity kicks or punches.
To learn how Sciatica is diagnosed Click Here
Cauda Equina Syndrome is an injury that occurs due to ruptured or herniated discs that are left untreated or poorly managed. UFC veteran Angela Magana, suffered the complication after her disc ruptured. She underwent surgery for a ruptured disc and slipped into a coma due to cauda equina syndrome. She woke a few days later, but it has paused her career as an MMA fighter for now.
Cauda equina syndrome occurs due to compression of the spinal cord, nerves, and nerve roots arising. They take place due to a herniated or ruptured lumbar intervertebral disc. The disc could be acutely damaged during a fight, or crush or it could be chronically due to stress that finally causes the disc to herniate.
To learn how Cauda Equina Syndrome are diagnosed Click Here
Common Injuries
Learn more about other common lower back injuries in our Common Injuries section.
Lower Back Injury Diagnosis
Lower back injuries are often put through a gamut of tests because spinal injuries can cause life-altering sequelae such as paralysis, paresis, and death. Imaging and physical exam form the cornerstone of diagnosing these injuries.
Injury Specific Diagnosis
Physical Exam
Sciatica is a clinical diagnosis. A good physical examination is needed to evaluate pain and symptoms. Sciatica demonstrates unilateral pain. On examination of the lower back and leg, pain radiates to the affected extremity.
Doctors must examine sensation and muscle strength in the buttocks and lower limbs. A straight-leg raise test is done. It is a passive examination. The fighter lies in a relaxed, supine position. The doctor lifts the then lifts the leg and flexes at the hip joint. The knee is kept extended or the leg is kept straight. Any pain in the back between 30 to 70⁰ of hip flexion is diagnostic of a lumbar disc herniation. Musculoskeletal causes reproduce pain above 70⁰ of flexion and below 30⁰ of flexion.
Imaging
Imaging is not done for sciatica. For fighters, it’s important to still get plain films of the lumbosacral spine. The doctors should assess fractures, disc rupture, herniation, or spondylolisthesis. A non-contrast CT scan is performed if plains films don’t reveal any findings. If the fighter continues to experience pain for more than 6 to 8 weeks and does not respond to treatment, an MRI is done. For all neurologic deficits, an MRI must be done to rule out any spinal pathology.
Lab Tests
Blood tests are not necessary to confirm sciatic unless surgery is warranted.
To learn how Sciatica is diagnosed Click Here
A thorough neurological examination is paramount when it comes to cauda equina syndrome. Any motor or sensory deficits in the legs whether bilateral or unilateral and asymmetrical raise a flag for spinal pathology.
Doctors look for signs like areflexia, hypotonia, atrophy seen in chronic compression to identify a herniating spinal cord. Additionally, saddle anesthesia in the buttock area, absent or decreased rectal tone and impotence in men will also be checked. Doctors will also palpate the bladder to see if there is urinary retention.
The gold standard is an urgent MRI imaging with sagittal and axial sequences. Early MRI is needed to proceed with surgery as cauda equina syndrome can be fatal. Neurosurgical or orthopedic consultation must follow. Ideally, an MRI must be done within an hour from the presentation. A CT myelogram is an option for those with metal implants and cannot do an MRI. A bladder scan is also done to check for post-void residual volume. This is to evaluate any urinary retention.
Blood tests are done in preparation for surgery. A lumbar puncture is diagnostic. It evaluates the contents of the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for blood and infection. It can determine the pressure within the central nervous system. It involves inserting a needle between the vertebrae at the L4 level through the dura. Cerebrospinal fluid is tapped and then sent for testing.
To learn how Cauda Equina Syndrome are diagnosed Click Here
Common Diagnoses
Read our Common Diagnoses section to understand how doctors diagnose injuries in the lower back through various tests and modalities.
Lower Back Injury Treatment
Lower back injuries are treated based on the injury. Most lower back injury management involves strengthening the core muscles and practicing good technique to prevent them. Injuries to the back are dangerous since they can damage the spinal column and lead to cauda equina syndrome which can be fatal. Treatments for this injury always involve surgery.
Injury Specific Treatment
Emergency
This is not a medical emergency. Fighters tend to fight and work through this pain. However, if bowel and bladder functions are affected the fighter mist visit with a doctor immediately.
Medical
A short course of oral NSAIDs is started to manage pain. Opioid and nonopioid analgesics are advised for those with severe pain. Muscle relaxants are given to those dealing with muscle stiffness. Anticonvulsants are prescribed for neurogenic pain. If all these pain management medications fail, then a short course of oral corticosteroids is given. Localized corticosteroid injections are also another alternative. Additionally, deep tissue massages and physical therapy are also advised to relieve the muscles. Surgical therapy is advised for disc herniation and spinal stenosis.
Home
At home, fighters are advised to use hot or cold packs to decrease inflammation. They should avoid activities that would trigger or incite pain. Additionally, avoid sitting or standing for prolonged

periods. Practice a good posture. Develop core strength and back muscles. Warm-up before all workouts. Stretch the lumbar spine and hamstrings gradually into your routine. If you lift weights, learn proper lifting techniques. Light exercises like swimming, walking, and aquatherapy can ease the tension in the muscles.
Following ATLAS guidelines, an immediate neurosurgical consult is important. Simultaneously, orthopedic consult must be sought. After an immediate MRI surgery must follow.
The treatment is surgical decompression via laminectomy. This could involve subsequent discectomy or not, or via sequestrectomy. A laminectomy is where the back portion of the vertebra is removed to ease the pressure on the spine. A discectomy is where the disc is completely removed and replaced with a synthetic disc or it could be partially removed.
Post cauda equina syndrome surgery, the recovery is long. Ice the incision area for 20-30 minutes several times a day. Always wrap the ice in a towel. Keep the incision clean and dry.

Change position every 45-60 minutes while awake. Walk three times a day or as permitted. Don’t do any strenuous activity. No sports or aerobic activity that involves lifting, bending, and jarring the spine. Don’t limit movement either.
No lifting more than 10 pounds are permitted. No driving until all reflexes have returned. Sex is not permitted for two weeks after surgery. Sleep on the side.
Place pillows behind the knees if lying on your back. Alternatively, place pillows behind the back and between the legs when lying on one side. No swimming, hot tubs, and lakes until 6 weeks post-surgery to keep the incision dry and uninfected. Wear compression stockings and elevate legs to increase circulation. Pain management NSAIDs or opiate medications as needed.
Common Treatments
Read through our Common Treatments section to understand how various back injuries are treated through conservative and alternative therapies.
